gran model hertz/lubricated¶
Syntax¶
model hertz/lubricated [other model_type/model_name pairs as described here ] keyword values
zero or more keyword/value pairs may be appended
limitForce values = 'on' or 'off' on = ensures that the normal force is never attractive (an artefact that can occur at the end of a collision). off = standard implementation that might lead to attractive forces. tangential_damping values = 'on' or 'off' on = activates tangential damping off = no tangential damping correctYoungsModulus values = 'on' or 'off' on = uses youngsModulusOriginal for approach distance calculation off = uses youngsModulus for approach distance calculation
LIGGGHTS vs. LAMMPS Info:
This part of pair gran and fix wall/gran is not available in LAMMPS.
Description¶
This granular model combines the contact force calculation of normal model hertz with lubrication force calculation. It is designed to be used in conjunction with tangential model history/lubricated.
During the approach of two particles, the minimum approach distance between their surfaces is calculated. This is governed either by their surface roughness, or by their elastic deformation during the lubricated collision. By using the correctYoungsModulus keyword, the minimum approach distance calculation can be performed using the original Youngs modulus, while the contact force calculation is performed using a lower Youngs modulus. The viscosity of the interstial liquid is set by fix property/atom fluidViscosity. In a coupled simulations, this can be performed through fix cfd/coupling/fluidproperties.
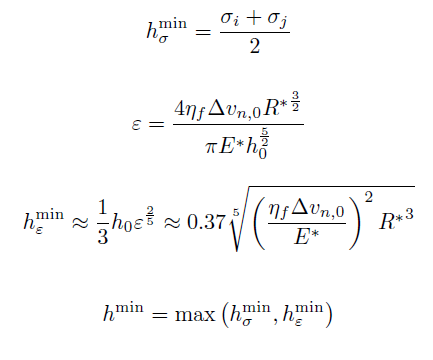
The total normal force is a combination of the lubrication force and the contact force. For calculation of the contact force, see normal model hertz. The lubrication force is calculated untill the cut-off distance h_co, which is set by property/global lubricationCutoff. Please note that lubricationCutoff is expressed as a multiple of the reduced radius R*. A value of lubricationCutoff = 1.0 (i.e. h_co = R*) is recommended. The neighbourlist skin distance must be set large enough to include this cut-off distance, see neighbor.
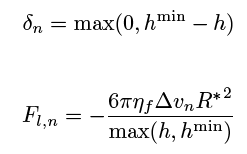
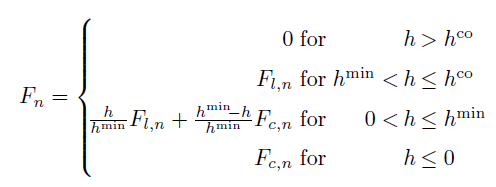
The quantities in the equations are as follows:
h^min_sigma = minimum approach distance due to surface roughness
h^min_epsilon = minimum approach distance due to deformation
h^min = minimum approach distance
h = |r| - (R_i + R_j) = gap height
h_0 = initial gap height
sigma = surface roughness
epsilon = elastic parameter
eta_f = fluid viscosity
R* = R_i*R_j/(R_i + R_j)reduced radius
E* = Y* = reduced Youngs Modulus (see normal model hertz)
Delta v_n = normal velocity
Delta v_n,0 = normal approach velocity
delta_n = overlap distance of 2 particles
F_c = contact force
F_l = lubrication force
F_n = total normal force
To define those material properties, it is mandatory to use multiple fix property/global and fix property/atom commands:
fix id all property/global youngsModulus peratomtype value_1 value_2 ...
(value_i=value for Youngs Modulus of atom type i)
fix id all property/global youngsModulusOriginal peratomtype value_1 value_2 ...
(value_i=value for original Youngs Modulus of atom type i)
fix id all property/global poissonsRatio peratomtype value_1 value_2 ...
(value_i=value for Poisson ratio of atom type i)
fix id all property/global coefficientRestitution peratomtypepair n_atomtypes value_11 value_12 .. value_21 value_22 .. .
(value_ij=value for the coefficient of restitution between atom type i and j; n_atomtypes is the number of atom types you want to use in your simulation)
fix id all property/global coefficientFriction peratomtypepair n_atomtypes value_11 value_12 .. value_21 value_22 .. .
(value_ij=value for the (static) coefficient of friction between atom type i and j; n_atomtypes is the number of atom types you want to use in your simulation)
fix id all property/global coefficientFrictionLubricated peratomtypepair n_atomtypes value_11 value_12 .. value_21 value_22 .. .
(value_ij=value for the (static) lubricated coefficient of friction between atom type i and j; n_atomtypes is the number of atom types you want to use in your simulation)
fix id all property/global surfaceRoughness peratomtype value_1 value_2 ...
(value_i=value for surface roughness of atom type i)
fix id all property/atom fluidViscosity scalar yes yes no value
(value=value for the (dynamic) fluid viscosity)
fix id all property/global lubricationCutoff scalar value
(value=value for cutoff distance of lubrication force calculation, expressed as a multiple of the reduced radius)
Warning
You have to use atom styles beginning from 1, e.g. 1,2,3,…
Force Limiting:
Note, that not using limitForce might lead to attractive forces between particles and walls, especially in case the coefficient of restitution is small. Be sure you include this key word for the pair style and the wall model if you like to avoid this.
Restrictions¶
If using SI units, youngsModulus must be > 5e6 If using CGS units, youngsModulus must be > 5e5 When using the limitForce, the specified coefficient of restitution is only approximate. This might become problematic for low coefficients of restitution as shown in Schwager and Poschel.
Default¶
tangential_damping = ‘on’ limitForce = ‘off’ correctYoungsModulus = ‘off’