fix heat/gran/radiation command¶
Syntax¶
fix ID group-ID heat/gran/radiation initial_temperature T0 keyword values
ID, group-ID are documented in fix command
heat/gran/radiation = style name of this fix command
initial_temperature = obligatory keyword
T0 = initial (default) temperature for the particles
zero or more keyword/value pairs may be appended
background_temperature value = T T = temperature of background max_bounces value = N N = maximum number of times a ray is reflected from a particle
Examples¶
fix radID all heat/gran/radiation initial_temperature 273.15
fix radID all heat/gran/radiation initial_temperature 450. background_temperature 300. max_bounces 100
LIGGGHTS vs. LAMMPS info:
This command is not available in LAMMPS.
Description¶
Calculates heat radiation between particles and temperature update according to Stefan Boltzmann’s Law:
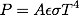
where P is the radiative power, A the surface area of the particle, epsilon the thermal emissivity of the particle, sigma Stefan Boltzmann’s constant and T the temperature of the particle in Kelvin.
Every timestep every particle radiates one ray. If the ray hits another particle part of the flux is absorbed and part of it is reflected in a random direction (see assumption: diffuse surface of particles).
It is assumed that:
the temperature within the particles is uniform.
emissivity is not wavelength-dependent
particles have perfectly diffuse surfaces
To make particles adiabatic (so they do not change the temperature due to this fix), set their thermal emissivity to 0.0. Thermal emissivity and specific thermal capacity must be defined for each atom type used in the simulation by means of fix property/global commands:
fix id all property/global thermalCapacity peratomtype value_1 value_2 ...
(value_i=value for thermal capacity of atom type i)
fix id all property/global thermalEmissivity peratomtype value_1 value_2 ...
(value_i=value for thermal emissivity of atom type i)
To set the temperature for a group of particles, you can use the set command with keyword property/atom and values Temp T. T is the temperature value you want the particles to have. To set heat sources (or sinks) for a group of particles, you can also use the set command with the set keyword: property/atom and the set values: heatSource h where h is the heat source value you want the particles to have (in Energy/time units). A negative value means it is a heat sink. Examples would be:
set region halfbed property/peratom Temp 800.
set region srcreg property/peratom heatSource 0.5
Output info:
You can visualize the heat sources by accessing f_heatSource[0], and the heatFluxes by f_heatFlux[0] . With f_Temp[0] you can access the per-particle temperature. You can also access the total thermal energy of the fix group (useful for the thermo command) with f_id .
Restart, fix_modify, run start/stop, minimize info:
The particle temperature and heat source is written to binary restart files so simulations can continue properly. None of the fix_modify options are relevant to this fix.
This fix computes a scalar which can be accessed by various output commands. This scalar is the total thermal energy of the fix group
No parameter of this fix can be used with the start/stop keywords of the run command. This fix is not invoked during energy minimization.
Restrictions¶
The fix group for this command
Default¶
background_temperature = initial_temperature max_bounces = 100